How Do Primary and Secondary Active Transport Mechanisms Differ
Membranous nephropathy MN consists of cases with unknown etiology primary MNPMN or idiopathic MNIMN and incidences caused by other conditions secondary MNSMN including cancers infections such as hepatitis B drug reactions and autoimmune diseases such as lupus. 4 The entry of the drug is prevented at the cell membranecell wall level.
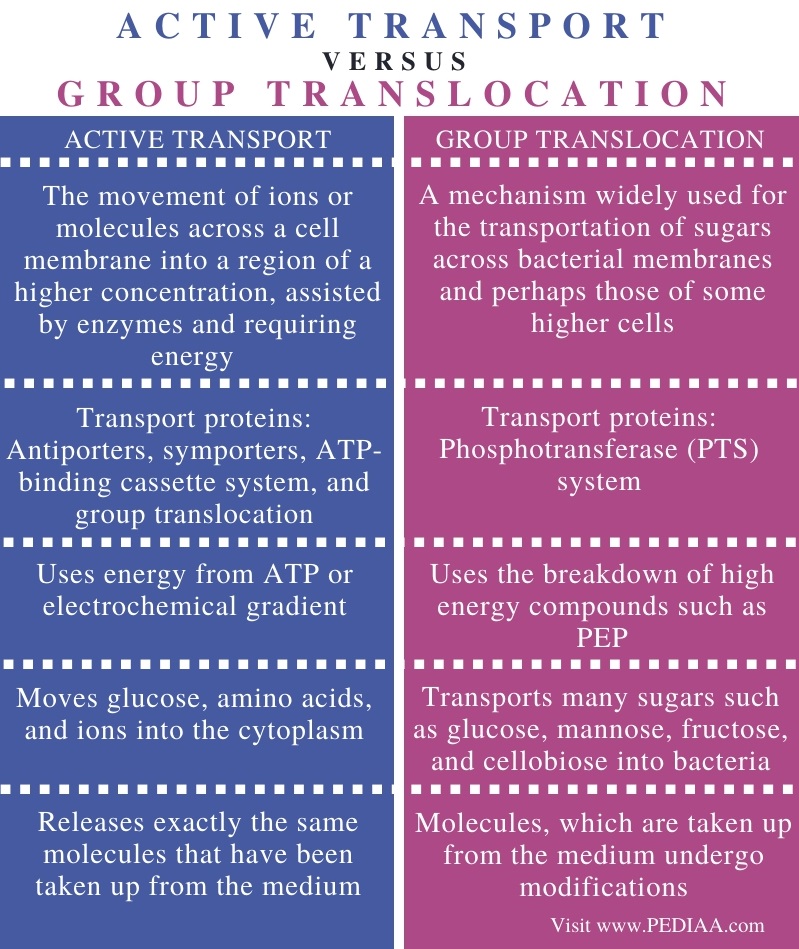
What Is The Difference Between Active Transport And Group Translocation Pediaa Com
5 The cell has.

. PMNs and SMNs constitute approximately 7580 and. 1 The target enzyme is overproduced so that the drug does not inhibit the biochemical reaction completely. 2 The drug target is altered so that the drug cannot bind to the target.
Mechanisms by which microbial cells might develop resistance. 3 The drug is pumped out by an efflux pump.
Difference Between Primary And Secondary Active Transport Definition Types Characteristics Similarities Differences

Active Transport Primary And Secondary Youtube
Difference Between Primary And Secondary Active Transport Definition Types Characteristics Similarities Differences

No comments for "How Do Primary and Secondary Active Transport Mechanisms Differ"
Post a Comment